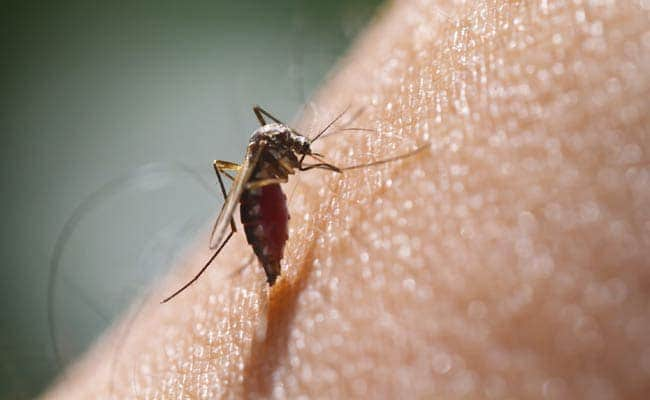
Dengue fever, a viral illness transmitted primarily by Aedes mosquitoes, poses a significant health risk in many parts of the world. In order to effectively mitigate this threat, it is crucial to implement comprehensive mosquito control strategies. By understanding the lifecycle of Aedes mosquitoes, recognizing factors that contribute to mosquito breeding, and employing various control methods, we can significantly reduce dengue transmission and protect public health.
Understanding Dengue
Dengue is a viral infection caused by the dengue virus and is primarily transmitted through the bites of infected female Aedes mosquitoes, mainly Aedes aegypti. The virus can lead to a wide spectrum of symptoms, from mild fever to severe flu-like illness, and in some cases, it can progress to a life-threatening condition known as severe dengue or dengue hemorrhagic fever.
Mosquito Species Carrying Dengue
Aedes mosquitoes are the primary vectors responsible for transmitting the dengue virus to humans. Aedes aegypti, often found in urban environments, and Aedes albopictus, commonly known as the Asian tiger mosquito, are the main culprits. These mosquitoes are well adapted to human habitation, making control efforts challenging.
Lifecycle of Aedes Mosquitoes
Understanding the lifecycle of Aedes mosquitoes is essential for effective control. The lifecycle includes four stages: egg, larva, pupa, and adult. Eliminating or disrupting breeding at any of these stages can significantly reduce mosquito populations. Eggs, for instance, are often laid in water containers and can survive without water for months, hatching when conditions are suitable.
Factors Promoting Mosquito Breeding
Several factors contribute to mosquito breeding. Stagnant water in containers, poor waste management, and neglected water storage sites provide ideal breeding grounds for Aedes mosquitoes. Warm and humid climates further facilitate rapid mosquito reproduction.
Dangers of Dengue
Dengue can have serious health implications, ranging from high fever and joint pain to organ impairment and, in severe cases, death. It poses a considerable burden on healthcare systems in endemic regions and can lead to economic losses due to medical costs and reduced productivity.
Integrated Mosquito Management (IMM)
Integrated Mosquito Management (IMM) is a holistic approach to mosquito control that combines various strategies. These include source reduction (eliminating breeding sites), biological control (introducing natural predators), and chemical control (using safe insecticides).
Personal Protection Measures
Individuals can play a vital role in preventing dengue by protecting themselves from mosquito bites. Wearing long sleeves, using insect repellents, and sleeping under bed nets are effective measures.
Elimination of Breeding Sites
Reducing mosquito breeding sites around homes and communities is a key preventive measure. Regularly emptying containers that collect water, covering water storage containers, and maintaining clean surroundings can significantly reduce Aedes mosquito populations.
Biological Control Methods
Introducing natural predators of mosquitoes, such as certain fish species and dragonfly larvae, can help keep mosquito populations in check. Additionally, using biological agents like Bacillus thuringiensis israelensis (BTI) bacteria can target mosquito larvae without harming other organisms.
Chemical Control Measures
The judicious use of insecticides is another aspect of mosquito control. Insecticides can be applied to areas with high mosquito activity, such as breeding sites and resting places. However, careful consideration of environmental and health impacts is essential.
Community Involvement
Community participation is integral to the success of mosquito control efforts. Public awareness campaigns, community clean-up drives, and cooperation with local authorities can create a united front against dengue.
Innovative Technologies
Technological advancements have revolutionized mosquito control. Drones equipped with sensors can identify potential breeding sites, and data-driven approaches help target control measures precisely.
Government Initiatives
Governmental organizations play a crucial role in dengue prevention. They enact policies, allocate resources, and coordinate large-scale control efforts to minimize dengue’s impact on public health.
Global Efforts and Conclusion
Dengue is a global concern, and international collaboration is essential. Organizations like the World Health Organization (WHO) work with governments and communities to share best practices and implement effective dengue prevention strategies.
In conclusion, controlling mosquitoes for dengue prevention requires a multifaceted approach. By understanding the biology of Aedes mosquitoes, addressing breeding sites, using innovative technologies, and involving communities and governments, we can make significant strides in reducing dengue transmission and safeguarding public health.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is dengue fever?
Dengue fever is a viral illness transmitted by Aedes mosquitoes, causing symptoms ranging from mild fever to severe flu-like conditions.
How can I protect myself from mosquito bites?
Wear protective clothing, use insect repellents, and sleep under bed nets to avoid mosquito bites.
What is Integrated Mosquito Management (IMM)?
IMM is a comprehensive approach to mosquito control that combines various strategies like source reduction, biological control, and chemical control.
Are there natural ways to control mosquito populations?
Yes, introducing natural predators like fish and using bacterial agents like BTI can help control mosquito larvae.
How can communities contribute to dengue prevention?
Communities can participate through public awareness campaigns, clean-up drives, and cooperation with local authorities.